Means of Protection
MOP, MOOP, and MOPP. These might sound like Muppet names, but they are actually at the heart of medical device design. The purpose of a medical device is to help a patient be well, so the device should not do harm.
In medical device design, MOP stands for Means of Protection and refers to the steps taken to keep patients safe from electrical shock around medical electrical equipment.
The widely recognized EN 60601-1 standard for medical electrical equipment defines a Means of Protection as a means for reducing the risk of electric shock to its requirements. To be considered a MOP, EN 60601-1 defines the types of isolation barriers and acceptable levels of leakage current.
Types of MOP — MOOP and MOPP
In the 60601-1 standard MOPP and MOOP are specific kinds of means of protection — Means of Operator Protection and Means of Patient Protection.
- Means of Operator Protection (MOOP) are the means of reducing the risk of electrical shock to people other than the patient, like the operator of the device.
- Means of Patient Protection (MOPP) are the means of reducing the risk of electrical shock to the patient. MOPP standards are stricter than MOOP standards, because of the potentially vulnerable condition of patients. Achieving MOPP standards will protect both patients and non-patients (“operators”).
Ways to Meet MOP Standards
A Means of Protection is an isolation barrier between electrical circuits that meets 60601-1 requirements. The standard calls for using one or more methods for achieving Means of Protection, which include:
- Solid Insulation: Solid insulation that complies with the dielectric strength test specified in the standard.
- Air Clearance: The shortest distance through air between two conductive parts allowed by the standard.
- Creepage Distance: The shortest distance along the surface of the insulating material between two conductive parts allowed by the standard.
- Protective Earth Connections: Protective earth ground connections protect the operator or patient from shock hazards by conducting leakage current safely to earth. A fuse or circuit breaker, when included on a device, is considered a MOP.
Test Conditions for MOP Levels
Means of Protection are tested with medical electrical equipment under two sets of circumstances: Normal and Single-Fault Conditions.
- Normal Condition (NC): All Means of Protection remain intact during testing, with leakage current staying within allowable limits. NC testing is done to verify that protection is still in place during normal operating conditions.
- Single Fault Condition (SFC): When one (but only one) of the Means of Protection is removed, and the leakage current remains within limits. This is usually done by removing the earth ground connection. SFC testing is done to verify that if one MOP should fail, a second MOP will still keep the patient and operator safe.
Two Levels of MOOP and MOPP
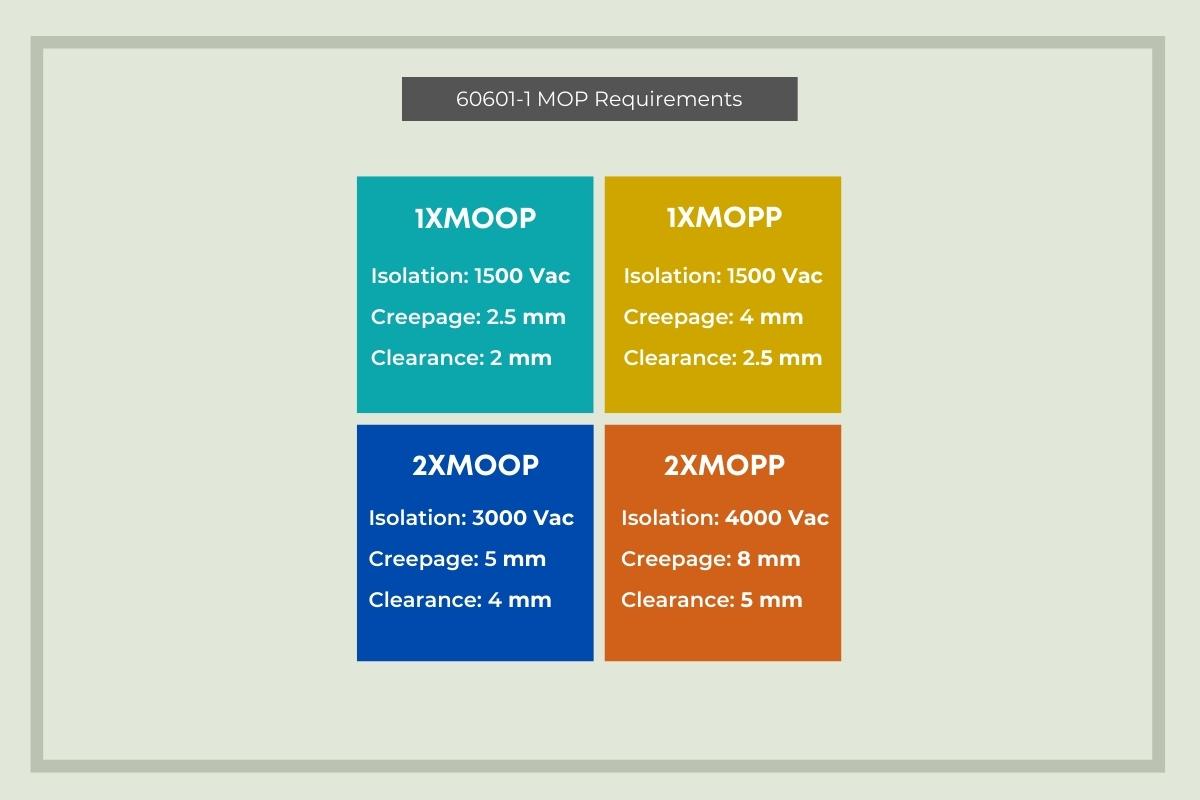
The EN 60601-1 standard defines two levels of Means of Protection from electrical hazards that medical electrical equipment can achieve; the allowable level depends on a device’s specific use. Independent laboratories will measure performance and check component specifications for a device and then certify the MOP level. The process for determining the level of MOOP and MOPP achieved are similar, but MOPP classification calls for stricter requirements.
One MOP Level (1xMOP): Basic protection against electric shock is present.
Two MOP Level (2xMOP): Enhanced insulation (double or reinforced insulation) is present, in case the first level of MOP fails.
A PC-based medical device used with patients should meet 2xMOPP requirements. using a power supply rated to 1xMOPP plus an isolation transformer can get you there. However, transformers can be bulky and add expense. Using a power supply rated to 2xMOPP is a smaller, easier solution.
Protection in Medical Power Supplies
All power supplies meet safety standards of some sort. However, those used in medical electrical equipment (whether in hospitals, clinics, or home healthcare settings) must meet strict MOP requirements to prevent shock hazards.
The safest choice is to use a certified medical power supply that meets the 2xMOPP standard.
________________________
RAM medical power supplies are designed and certified for robust 2xMOPP protection. Contact us for details.